Okay, let’s be real. When you hear a headline like “NASA Attempts Rescue as Space Telescope Descends to Earth,” your brain probably jumps to a few places: impending doom, maybe a massive fireball, or the sudden end of stunning space photography. But the reality, as is often the case with space news, is a bit more nuanced – and fascinating. This isn’t about a telescope crashing down in a fiery spectacle. It’s more like a delicate, high-stakes operation to save one of our most important eyes on the cosmos. We’re diving into the James Webb Space Telescope situation, its unexpected descent, and why NASA is hustling to fix it. This is the “Why” angle, by the way. Understanding the significance behind the headlines. Why does this matter to you, sitting there in India?
Why This Space Telescope Situation Matters – Especially to You
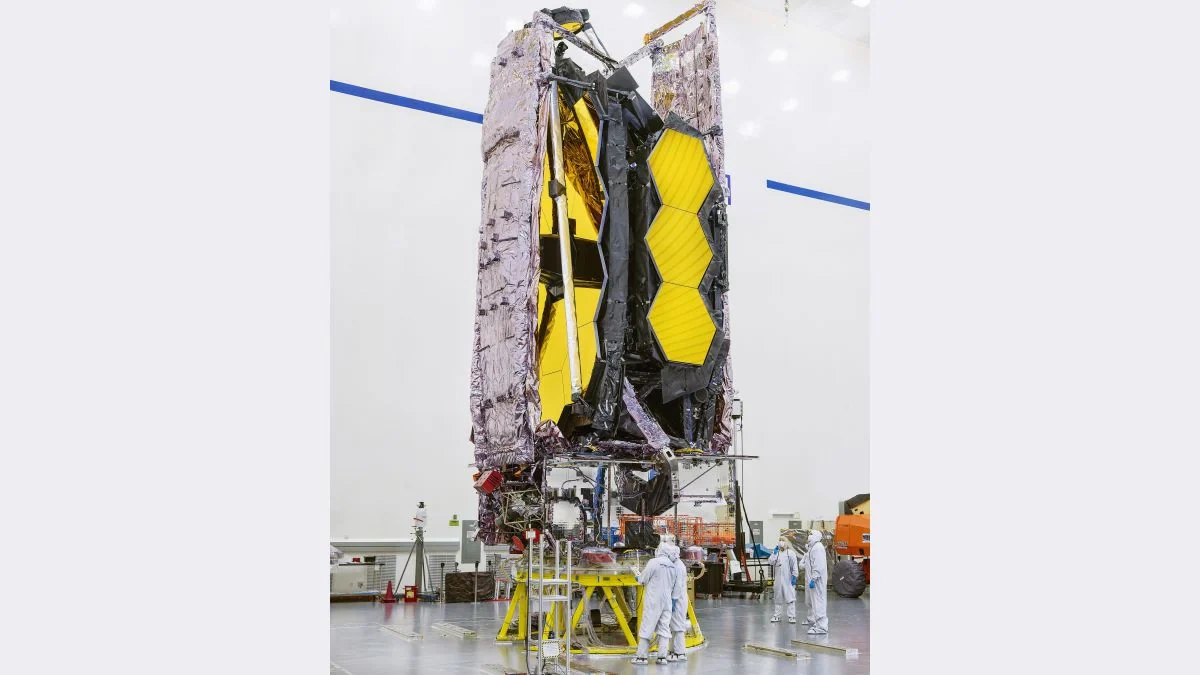

Here’s the thing: space exploration isn’t just some abstract, sci-fi fantasy. The data collected by telescopes like the Hubble’s successor, the JWST telescope , impacts our understanding of the universe, leading to breakthroughs in technology, medicine, and countless other fields. The images and data help to understand the cosmic phenomena and also analyze exoplanets and their atmospheres to better understand their possibility to inhabit life.
So, when a space telescope faces a problem, it’s not just a setback for NASA; it’s a potential slowdown in scientific progress. The recent issue with the telescope’s altitude is a prime example. The telescope’s orbit is decaying due to atmospheric drag. While it’s still operational, the rate of descent has increased, prompting NASA to take action. But, why is this happening now?
Well, as per the European Space Agency, the Sun is currently in a period of increased solar activity. This activity causes the Earth’s atmosphere to expand, increasing drag on objects in low Earth orbit. So what does that mean? Satellites and, yes, even our beloved space telescope experience more friction as they move through this thicker atmosphere, causing them to lose altitude. This phenomenon is also called solar maximum .
The Rescue Plan | What NASA is Doing
Alright, let’s get into the specifics. NASA isn’t just sitting around wringing their hands. They’re implementing a series of maneuvers to boost the telescope’s altitude . These maneuvers involve using the telescope’s onboard thrusters to counteract the atmospheric drag and nudge it back into its intended orbit. I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized the precision involved is mind-boggling. We’re talking about fine-tuning a multi-billion-dollar piece of equipment that’s hundreds of kilometers above us.
The frequency of these maneuvers has increased in recent months, indicating the growing concern over the telescope’s orbital decay . NASA engineers are constantly monitoring the situation and adjusting their strategies as needed. The goal is to maintain the space telescope’s orbit at a stable altitude, ensuring it can continue its observations without interruption. You can follow the updates on NASA’s official website (https://www.nasa.gov/ ).
The Long-Term Implications and What’s Next
But, the question remains, what does this mean for the future? This situation highlights the ongoing challenges of maintaining satellites and space telescopes in low Earth orbit. Atmospheric drag is a constant factor that needs to be accounted for, especially during periods of increased solar activity.
Looking ahead, NASA and other space agencies are exploring new technologies and strategies to mitigate the effects of atmospheric drag. This includes developing more efficient thrusters, using lighter materials to reduce the mass of satellites, and even exploring the possibility of actively removing debris from low Earth orbit. Let me rephrase that for clarity: This isn’t just about saving one telescope; it’s about ensuring the long-term sustainability of space exploration.
And, what fascinates me is how this seemingly distant problem connects to our daily lives. The technologies developed for space exploration often have trickle-down effects, leading to innovations in areas like telecommunications, medicine, and materials science. So, the next time you hear about a space telescope facing a challenge, remember that it’s not just a story about space; it’s a story about human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge. Consider reading this fascinating article about the Moon’s origin .
It’s also worth noting that the data collected by the Hubble space telescope and James Webb Space Telescope are publicly available, allowing scientists from around the world, including India, to conduct their own research and make new discoveries. This collaborative approach is essential for advancing our understanding of the universe. It is also possible to download some of the pictures and use them as wallpapers or screensavers. I am thinking about downloading some myself.
Why Redundancy and Replacements are Key
Let’s be honest, space is hard. Equipment fails, orbits decay, and unexpected problems arise. That’s why redundancy and planning for replacements are crucial. The James Webb Space Telescope , while incredibly powerful, isn’t going to last forever. NASA is already thinking about the next generation of space telescopes that will build upon the successes of Hubble and JWST. It is expected that the next generation of space telescopes will use advanced materials and artificial intelligence to provide even clearer images and data.
These future telescopes may be designed to operate in higher orbits, where atmospheric drag is less of a factor, or they may incorporate technologies that allow them to be easily refueled and repaired in space. The key is to learn from the challenges faced by current telescopes and to develop more resilient and sustainable systems for future exploration. For example, a common mistake I see people make is assuming that because something worked for Hubble, it will automatically work for JWST. But each space telescope has its unique quirks and challenges.
In fact, the success of the Hubble paved the way for the development of more advanced space telescopes , like the Spitzer space telescope and the Chandra x-ray observatory , each designed to observe the universe in different wavelengths of light. These observatories have provided complementary data that have revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Don’t forget to explore other interesting topics, such as comet alien technology .
Orbital Mechanics and Atmospheric Drag Explained Simply
Okay, let’s break down the science a bit. Orbital mechanics , at its core, is about the interplay between gravity and inertia. A space telescope stays in orbit because its forward motion is constantly counteracted by Earth’s gravity, causing it to fall around the planet rather than crashing into it. But here’s where atmospheric drag comes in.
Even in the upper reaches of the atmosphere, there are still trace amounts of air molecules. As the telescope moves through these molecules, it experiences friction, which slows it down ever so slightly. Over time, this slowdown causes the telescope to lose altitude, eventually leading to orbital decay. Think of it like a bicycle tire slowly losing air – you need to pump it up periodically to maintain the correct pressure.
The amount of atmospheric drag depends on several factors, including the telescope’s size and shape, its altitude, and the density of the atmosphere. Solar activity can also have a significant impact, as increased solar radiation heats up the atmosphere and causes it to expand. All these factors are carefully considered by NASA engineers when planning and executing orbital maneuvers.
FAQ | Your Burning Questions Answered
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly does “orbital decay” mean?
It means the space telescope is gradually losing altitude and getting closer to Earth due to atmospheric drag.
Is the telescope in danger of crashing?
Not imminently. NASA is actively working to counteract the orbital decay.
How often does NASA have to perform these rescue maneuvers?
The frequency has increased recently due to heightened solar activity. It’s constantly monitored and adjusted.
Can the public track the telescope’s location?
Yes, you can find real-time tracking information on various space tracking websites.
What happens if NASA can’t maintain its orbit?
Eventually, it would re-enter the atmosphere. But NASA is taking steps to prevent that.
Will this affect the quality of the telescope’s images?
Not significantly, as long as NASA can maintain a stable orbit.
Ultimately, the story of NASA’s rescue attempt is a reminder of the delicate balance required to explore the cosmos. It’s a testament to human ingenuity, our relentless pursuit of knowledge, and our unwavering commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. And, maybe, just maybe, it will inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers in India to reach for the stars.


Leave feedback about this